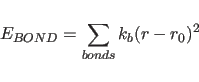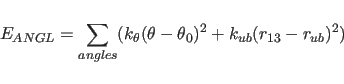| bit | Xplor-NIH | VMD-XPLOR |
|---|
|
| Xplor-NIH home Documentation |
Next: Nonbonded Energy Terms Up: Energy Function Previous: Empirical Energy Functions
Conformational Energy Terms
The term
describes the covalent bond energy where the sum is carried out over all covalent bonds in the molecular structure selected by the constraints interaction statement;
The term
The angle between two planes,
the first being defined through atoms i,j,k and the second
through atoms j,k,l, is defined as a torsion angle where the
atoms i,j,k,l are specified by the dihedral and improper statements
(Section 3.1.1).
The terms
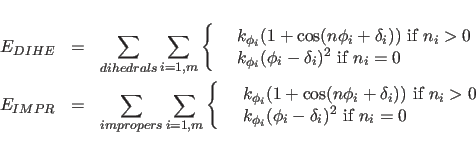
describe the dihedral and improper energy terms. The sums are carried out over all dihedral or improper angles in the molecular structure selected by the constraints interaction statement;
The specification of multiple dihedral or torsion angles with ![]() allows one to carry out a cosine expansion of a torsion potential
for a particular instance involving four atoms or four atom types.
Multiple dihedral angles and improper angles have to be indicated
by using the MULTiple option both in the definition of the molecule's
topology (Section 3.1.1) and in the
specification of the corresponding parameter
(Section 3.2.1). Internally, X-PLOR stores
multiple dihedral or improper angles as multiple instances of the
same combination of atoms or atom types.
allows one to carry out a cosine expansion of a torsion potential
for a particular instance involving four atoms or four atom types.
Multiple dihedral angles and improper angles have to be indicated
by using the MULTiple option both in the definition of the molecule's
topology (Section 3.1.1) and in the
specification of the corresponding parameter
(Section 3.2.1). Internally, X-PLOR stores
multiple dihedral or improper angles as multiple instances of the
same combination of atoms or atom types.
Xplor-NIH 2025-11-07