| bit | Xplor-NIH | VMD-XPLOR |
|---|
|
| Xplor-NIH home Documentation |
Next: Example: Topology of a Up: Topology Statement Previous: Topology Statement
Syntax
- TOPOlogy {
 topology-statement
topology-statement } END
} END - is invoked from the main level of X-PLOR.
 topology-statement
topology-statement :==
:==-
- AUTOgenerate
- ANGLe=
 logical
logical DIHEdral=
DIHEdral= logical
logical END
works only on regular residues,
not on patched ones. It automatically
generates all possible bond angles based on the connectivity list of the
particular residue. It operates on the residues following the statement
until the
next autogenerate statement appears.
END
works only on regular residues,
not on patched ones. It automatically
generates all possible bond angles based on the connectivity list of the
particular residue. It operates on the residues following the statement
until the
next autogenerate statement appears.
- MASS=
 type
type =
= real
real
- adds a default mass assignment for the specified type of atom to the topology database. The real number is defined in atomic mass units. This value will be used by default for all atoms of that type unless an explicit MASS statement is given in the atom statement (see below).
- RESEt
- erases all previous entries into the topology database.
- RESIdue
 residue-name
residue-name {
{  residue-statement
residue-statement } END
adds a residue to the topology database.
} END
adds a residue to the topology database.
- PRESidue
 residue-name
residue-name { [ ADD
{ [ ADD 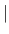 DELEte
DELEte 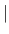 MODIfy ]
MODIfy ]
 residue-statement
residue-statement } END
adds a patch residue to the topology database.
} END
adds a patch residue to the topology database.
 residue-statement
residue-statement :==
:==-
- ACCEptor
 atom
atom
 atom
atom adds a hydrogen-bond acceptor
for the explicit hydrogen-bonding energy term or for purposes of analysis
to the residue database. The first atom is acceptor atom;
the second atom is antecedent atom and can be the string NONE.
adds a hydrogen-bond acceptor
for the explicit hydrogen-bonding energy term or for purposes of analysis
to the residue database. The first atom is acceptor atom;
the second atom is antecedent atom and can be the string NONE.
- ANGLe
 atom
atom
 atom
atom
 atom
atom adds a bond angle made by
the three atoms to the residue database.
It should not be used if autogenerate angles
are active.
adds a bond angle made by
the three atoms to the residue database.
It should not be used if autogenerate angles
are active.
- ATOM
- [
 patch-character
patch-character ]
]  atom
atom
 atom-statement
atom-statement END
adds an atom to the residue database.
The statement defines atom as a four-character string
specifying the name, and atom statement specifies atom type,
charge, and mass. The patch character is a 1-character string
and may be used only for PRESidue.
END
adds an atom to the residue database.
The statement defines atom as a four-character string
specifying the name, and atom statement specifies atom type,
charge, and mass. The patch character is a 1-character string
and may be used only for PRESidue.
- BOND
 atom
atom
 atom
atom adds a covalent
bond between the specified atoms to the residue database. The
atoms have
to be
defined previously by atom statements. Parameters for
the bond are specified in Section 3.2.1;
Eq. 4.4 describes the bond energy.
adds a covalent
bond between the specified atoms to the residue database. The
atoms have
to be
defined previously by atom statements. Parameters for
the bond are specified in Section 3.2.1;
Eq. 4.4 describes the bond energy.
- DIHEdral
 atom
atom
 atom
atom
 atom
atom
 atom
atom [MULTiple
[MULTiple  integer
integer ] adds
a dihedral angle to the residue database. The dihedral angle (ijkl)
is defined
by the angle between the plane made by the atoms (ijk) and the plane
made by the atoms (jkl). The dihedral statement
should not be used if autogenerate dihedrals are
active, unless multiple dihedral angles are wanted. MULTiple
specifies
] adds
a dihedral angle to the residue database. The dihedral angle (ijkl)
is defined
by the angle between the plane made by the atoms (ijk) and the plane
made by the atoms (jkl). The dihedral statement
should not be used if autogenerate dihedrals are
active, unless multiple dihedral angles are wanted. MULTiple
specifies 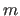 dihedral angle entries for the same instance
of four atoms (Eq. 4.6).
This allows one to specify a cosine expansion for the dihedral
angle potential energy.
It must be accompanied by a corresponding DIHEdral angle parameter
entry with appropriate multiplicity. Parameters for
the dihedral angle are specified in Section 3.2.1;
Eq. 4.6 describes the dihedral energy.
dihedral angle entries for the same instance
of four atoms (Eq. 4.6).
This allows one to specify a cosine expansion for the dihedral
angle potential energy.
It must be accompanied by a corresponding DIHEdral angle parameter
entry with appropriate multiplicity. Parameters for
the dihedral angle are specified in Section 3.2.1;
Eq. 4.6 describes the dihedral energy.
- DONOr
 atom
atom
 atom
atom adds a hydrogen-bond donor for
the explicit hydrogen-bonding energy term or for purposes of analysis
to the residue database.
The first atom is hydrogen atom, and the second atom is heavy atom; the
first
atom may be the string NONE for extended atom force fields.
Parameters for
the explicit hydrogen bonds are specified in
Section 3.2.1;
Eq. 4.25 describes the hydrogen-bond energy.
adds a hydrogen-bond donor for
the explicit hydrogen-bonding energy term or for purposes of analysis
to the residue database.
The first atom is hydrogen atom, and the second atom is heavy atom; the
first
atom may be the string NONE for extended atom force fields.
Parameters for
the explicit hydrogen bonds are specified in
Section 3.2.1;
Eq. 4.25 describes the hydrogen-bond energy.
- GROUp
- partitions the atoms into nonbonded groups
(see Section 4.3.3). In addition to use
for nonbonded interactions, grouping has an effect on atom order
for atoms added or modified in PATCh statements (Section 3.8).
- IMPRoper
 atom
atom
 atom
atom
 atom
atom
 atom
atom [MULTiple
[MULTiple  integer
integer ] adds
an improper angle to the residue database. The
definition is identical to the DIHEdral angle,
but it uses a different set of parameters
(cf. Section 3.2.1). As in the case of the DIHEdral
angle,
the improper angle (ijkl) is defined by the angle between the plane made by
the atoms (ijk) and the plane made by the atoms (jkl).
MULTiple
specifies
] adds
an improper angle to the residue database. The
definition is identical to the DIHEdral angle,
but it uses a different set of parameters
(cf. Section 3.2.1). As in the case of the DIHEdral
angle,
the improper angle (ijkl) is defined by the angle between the plane made by
the atoms (ijk) and the plane made by the atoms (jkl).
MULTiple
specifies 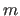 improper angle entries for the same
instance of four atoms (Eq. 4.6).
This allows one to specify a cosine expansion for the improper
angle potential energy.
It must be accompanied by a corresponding IMPRoper angle parameter
entry with appropriate multiplicity.
Parameters for
the improper angle are specified in Section 3.2.1;
Eq. 4.6 describes the improper energy.
improper angle entries for the same
instance of four atoms (Eq. 4.6).
This allows one to specify a cosine expansion for the improper
angle potential energy.
It must be accompanied by a corresponding IMPRoper angle parameter
entry with appropriate multiplicity.
Parameters for
the improper angle are specified in Section 3.2.1;
Eq. 4.6 describes the improper energy.
 atom
atom :==
:==- is the name of the atom; it is a four-character string.
 atom-statement
atom-statement :==
:==-
- CHARge=
 real
real
- specifies an electrostatic charge in units of one electron charge. This affects the electrostatic energy (Eq. 4.16).
- EXCLude=( {
 atom
atom } )
} ) - specifies explicit nonbonded interaction exclusions (see Section 4.3.3). The atoms have to have been defined previously by an atom statement.
- MASS=
 real
real
- overwrites a default given by mass statement outside residue statement, in atomic mass units.
- TYPE=
 type
type
- specifies the chemical atom type, a string with up to four characters. The atom type is used to retrieve type-based parameters (see Section 3.2.1).
- CHARge=
 type
type :==
:==- is any sequence of four characters.
