| bit | Xplor-NIH | VMD-XPLOR |
|---|
|
| Xplor-NIH home Documentation |
Next: Intramolecular Interactions Up: Nonbonded Energy Terms Previous: Van der Waals Function
Electrostatic Function
The electrostatic function is given by
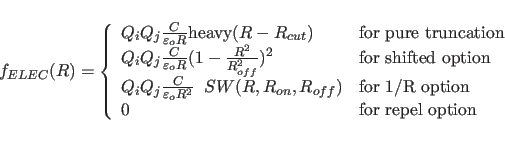
The electrostatic function is computed using the atomic
charges provided by the CHARge specification in the
atom statement
(see Section 3.1.1).
![]() is the dielectric constant, which can be defined by the
EPS statement;
is the dielectric constant, which can be defined by the
EPS statement; ![]() and
and ![]() are defined by the statements
CTONNB and CTOFNB respectively
(see Section 3.2.1).
Because of the need to limit the number of pair interactions and to avoid
discontinuities in the forces (to conserve energy during dynamics), several
schemes for truncating the electrostatic potential are used.
The
are defined by the statements
CTONNB and CTOFNB respectively
(see Section 3.2.1).
Because of the need to limit the number of pair interactions and to avoid
discontinuities in the forces (to conserve energy during dynamics), several
schemes for truncating the electrostatic potential are used.
The ![]() option
introduces an approximate solvent screening term
in the dielectric constant by
setting the constant equal to
option
introduces an approximate solvent screening term
in the dielectric constant by
setting the constant equal to
![]() .
The
.
The ![]() dielectric option was
originally developed because the execution of square roots was expensive on
certain obsolete computers. There is no physical justification for the 1/R
dielectric, but it is still in widespread use, in particular for simulations
in vacuum. The shifted option modifies the radial function so that the
energy and forces go to zero at the cutoff distance.
dielectric option was
originally developed because the execution of square roots was expensive on
certain obsolete computers. There is no physical justification for the 1/R
dielectric, but it is still in widespread use, in particular for simulations
in vacuum. The shifted option modifies the radial function so that the
energy and forces go to zero at the cutoff distance.
Xplor-NIH 2025-11-07
