| bit | Xplor-NIH | VMD-XPLOR |
|---|
|
| Xplor-NIH home Documentation |
Next: Requirements Up: Generating the Molecular Structure Previous: Generating the Molecular Structure
Syntax
 residue-number
residue-number
- specifies the number of a residue, a four-character string that can include nonnumerical characters.
 segment-name
segment-name
- specifies the name of a segment, a four-character string that can include nonnumerical characters.
- SEGMent {
 segment-statement
segment-statement } END
is invoked from the main level of X-PLOR.
} END
is invoked from the main level of X-PLOR.
 segment-statement
segment-statement :==
:==-
- CHAIn
- { [
 chain-statement
chain-statement ] } END
generates a sequence
of residues. The END statement activates the generation.
] } END
generates a sequence
of residues. The END statement activates the generation.
- MOLEcule
- NAME=
 residue-name
residue-name NUMBer=
NUMBer= integer
integer
END generates individual molecules such as in liquids (default of NUMBer is 1). The residue numbers are assigned sequentially, starting with 1. The residue name has to be defined in the topology statement (see Section 3.1.1). The END statement activates the generation of the molecules. - NAME=
 segment-name
segment-name
- specifies the segment name of all atoms to be generated using one of the following statements (default is “ ").
 chain-statement
chain-statement :==
:==-
- COORdinates {
 pdb-record
pdb-record } END
} END - takes a
sequence from a coordinate file.
It interprets the atom records of a PDB coordinate file in terms of the
sequence of the molecule. The residue numbers
are taken directly from the PDB coordinate file; they
do not have to be sequential. Note
that this statement does not actually read the x,y,z coordinates.
One should use the coordinate statement (Section
6.1) to read the coordinates. The
segment name has to match characters 73 through 76 in the
PDB coordinate file. (For the definition of
 pdb-record
pdb-record ,
see Section 6.1.)
,
see Section 6.1.)
- FIRSt
-
 residue-name
residue-name
TAIL= patch-character
patch-character =
= *residue-name*
*residue-name* END adds a special patch for the first residue in a sequence to
the chain database.
In the case of multiple statements,
equality has priority before wildcard matching; i.e.,
the more special assignments come first. The
chain database is reset each time the chain
statement is invoked.
END adds a special patch for the first residue in a sequence to
the chain database.
In the case of multiple statements,
equality has priority before wildcard matching; i.e.,
the more special assignments come first. The
chain database is reset each time the chain
statement is invoked.
- LAST
 residue-name
residue-name
HEAD= patch-character
patch-character =
= *residue-name*
*residue-name* END
adds a special patch for the last residue in a sequence to the
chain database.
In the case of multiple statements,
equality has priority before wildcard matching; i.e.,
the more special assignments come first. The
chain database is reset each time the chain
statement is invoked.
END
adds a special patch for the last residue in a sequence to the
chain database.
In the case of multiple statements,
equality has priority before wildcard matching; i.e.,
the more special assignments come first. The
chain database is reset each time the chain
statement is invoked.
- LINK
-
 residue-name
residue-name
HEAD= patch-character
patch-character =
= *residue-name*
*residue-name*
TAIL= patch-character
patch-character =
= *residue-name*
*residue-name* END
adds a special linkage patch to the chain database.
The statement will automatically connect residue
END
adds a special linkage patch to the chain database.
The statement will automatically connect residue 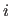 to residue
to residue 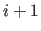 ; e.g.,
it creates a peptide linkage.
Wildcards are allowed for residue name.
In the case of multiple statements,
equality has priority before wildcard matching; i.e.,
the more special assignments come first. The
chain database is reset each time the chain
statement is invoked.
; e.g.,
it creates a peptide linkage.
Wildcards are allowed for residue name.
In the case of multiple statements,
equality has priority before wildcard matching; i.e.,
the more special assignments come first. The
chain database is reset each time the chain
statement is invoked.
- SEQUence {
 residue-name
residue-name } END
} END - takes the sequence as specified between the SEQUence and the END word. The residue numbers are assigned sequentially, starting with 1.
- COORdinates {
Xplor-NIH 2025-11-07
