| bit | Xplor-NIH | VMD-XPLOR |
|---|
|
| Xplor-NIH home Documentation |
Next: Syntax of the Pick Up: Analysis of Conformational Energy Previous: Analysis of Conformational Energy
Syntax of the Print Statement
- PRINt
 print-statement
print-statement
- is invoked from the main level of X-PLOR. Execution is activated as soon as all required statements are given.
 print-statement
print-statement :==
:==- [THREshold=
 real
real ]
]
 print-objects
print-objects prints objects. THREshold is optional
(default: THREshold=0).
prints objects. THREshold is optional
(default: THREshold=0).
 print-objects
print-objects :==
:==-
- ANGLes
- lists bond angles that deviate by more than the THREshold value from the equilibrium value in degrees; it also puts the value of the rms deviation into the symbol $RESULT and the number of violations into $VIOLATIONS.
- BONDs
- lists bond lengths that deviate by more than the THREshold value from the equilibrium value in Å; it also puts the value of the rms deviation into the symbol $RESULT and the number of violations into $VIOLATIONS.
- CDIHedrals
- lists dihedral angle restraints (see Section 7.2) that deviate by more than the THREshold value from the equilibrium value in degrees; it also puts the value of the rms deviation into the symbol $RESULT and the number of violations into $VIOLATIONS.
- DIHEdrals
- lists dihedral angles that deviate by more than the
THREshold
value from the equilibrium value in degrees; it
also puts the value of the rms deviation into the symbol
$RESULT and the number of violations into $VIOLATIONS. Multiple
dihedral angle entries (
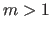 , Eq. 4.6) are
characterized by multiple instances of the same four atoms followed
by the corresponding parameters for the multiple dihedral.
, Eq. 4.6) are
characterized by multiple instances of the same four atoms followed
by the corresponding parameters for the multiple dihedral.
- HBONds
- lists hydrogen bonds between atoms that have been designated donors and acceptors (DONOr and ACCEptor; see Section 3.1.1) and that are within the cutoff limits specified in the hbonds statement (see Section 3.2.1). This facility can be used even if the current empirical energy function does not use explicit hydrogen-bonded terms. All that is required is to include the ACCEptor and DONOr statements in the residue statement (see Section 3.1.1) and the HBONded statements in the parameter statement.
- IMPRopers
- lists improper angles that deviate by more than the THREshold value from the equilibrium value in degrees; it also puts the value of the rms deviation into the symbol $RESULT and the number of violations into $VIOLATIONS.
- NOE
- lists distance restraints
(see Chapter 20)
that deviate by more than the THREshold value from the equilibrium value
in Å; it
also puts the value of the rms deviation into the symbol
$RESULT and the number of violations into $VIOLATIONS. The
definition of the deviation depends on which NOE POTEntial
is specified: in the case of the SQUAre-well and SOFTsquare
potentials, the deviation refers to the difference
between the actual distance and the upper or lower
bound if the distance is outside the error range; in
the case of the BIHArmonic potential,
the deviation refers to the difference between the actual
distance and the target distance.
(A more precise definition is
given by
 in Section 20.3.)
in Section 20.3.)
Xplor-NIH 2025-11-07
